The pregnancy period is a very important period in any couple's life, it is also a very complicated period. This total 9-month, wait to see a baby is really difficult and full of patience. Here the mother can feel the appearance of the baby in the womb but the father can't experience all such activity. Many of you are not aware of, how the fetal growth in the womb takes place in that 9 months, and what are the stages of prenatal development week by week, month by month and trimester by trimester. many of you are not aware of such an important point of prenatal development and we also cover embryonic development, fetal development, which is very important for new parents.
Before going into deep about prenatal development, let us understand the menstrual cycle. Most couples are unaware of the menstrual cycle and them unable to plan their baby accordingly, it also leads to an unplanned pregnancy.
Menstruation meaning refers to the periodic shedding of the uterine lining or refers to the discharge of blood and mucus from the uterus. It occurs in women from puberty till menopause, at regular intervals of about a month. The average menstrual or period cycle takes about 28 days. The time at which menstruation first begins it in girls is called menarche. It corresponds to the period of puberty. The release of the egg cell to the outer end of the uterine tube is called ovulation. Ovulation occurs midway of every menstrual cycle. The actual age at which cycle occur varies according to the individual's race, climate, social condition, health, etc. In India most girls begin to menstruate between the ages of 9 and 14 years, The duration of the cycle is 3-5 days.
Before going into deep about prenatal development, let us understand the menstrual cycle. Most couples are unaware of the menstrual cycle and them unable to plan their baby accordingly, it also leads to an unplanned pregnancy.
Menstrual Cycle
Females of reproductive age experiencing cycles of hormonal activity that repeat at about one-month intervals.[Menstru means "monthly"; hence the term menstrual cycle].Menstruation meaning refers to the periodic shedding of the uterine lining or refers to the discharge of blood and mucus from the uterus. It occurs in women from puberty till menopause, at regular intervals of about a month. The average menstrual or period cycle takes about 28 days. The time at which menstruation first begins it in girls is called menarche. It corresponds to the period of puberty. The release of the egg cell to the outer end of the uterine tube is called ovulation. Ovulation occurs midway of every menstrual cycle. The actual age at which cycle occur varies according to the individual's race, climate, social condition, health, etc. In India most girls begin to menstruate between the ages of 9 and 14 years, The duration of the cycle is 3-5 days.
- Changes during puberty.
Puberty is the time when there are a lot of hormonal changes in a girl are observed, changes are not only physically but also psychologically. These changes are divided into primary and secondary changes of puberty.
Primary changes are easily noticed, like all physical changes that occur are, changes in height weight, breast size, pimples and acne on the skin. The body produces more sweat giving out a body odor, hair grew under public areas like arms, legs and also vaginal discharge begins. The secondary changes are like psychological changes such as increased shyness, feeling of the reserve, mood swings, and awakening of sexual feelings are experienced.
There is a condition called Precocious puberty, which is early puberty which is a condition when puberty occurs at an early age.
Many girls worried that cycles are irregular at the beginning. But this is normal. It takes a while for the body to settle, which could be a few years after the cycle becomes regular. Many girls face the Menorrhagia, which is abnormally heavy bleeding during the period cycle. Periodic headaches and general upsets of health and stomach pain are common. Cramps are also normal. They can be relieved by keeping a hot water bag, taking a bath with warm water or doing gentle exercises.
Primary changes are easily noticed, like all physical changes that occur are, changes in height weight, breast size, pimples and acne on the skin. The body produces more sweat giving out a body odor, hair grew under public areas like arms, legs and also vaginal discharge begins. The secondary changes are like psychological changes such as increased shyness, feeling of the reserve, mood swings, and awakening of sexual feelings are experienced.
There is a condition called Precocious puberty, which is early puberty which is a condition when puberty occurs at an early age.
Many girls worried that cycles are irregular at the beginning. But this is normal. It takes a while for the body to settle, which could be a few years after the cycle becomes regular. Many girls face the Menorrhagia, which is abnormally heavy bleeding during the period cycle. Periodic headaches and general upsets of health and stomach pain are common. Cramps are also normal. They can be relieved by keeping a hot water bag, taking a bath with warm water or doing gentle exercises.
- Care during menses/Mensturartion.
Though the menstrual cycle is a natural process. It is necessary for girls to have habits of physical hygiene right from childhood. It is important to take special care during the period od menstruation which is as follows:-
- If the menstrual cycle is not regular or extends, has pain, heavy periods or very little bleeding, then doctors' advice should be taken.
- The bath should be taken twice a day with warm water.
- In olden days women would use cotton pad which was not enough protection. It could be embarrassing as it could be smelly, sometimes could leak and stain. So sanitary pads should be used. It should be changed every 3/4 hrs, or as per flow if the flow is more than changed accordingly. One should always clean the hands with soap after using them. It should be disposed of in a safe manner by wrapping it in a paper and putting it in the waste bins.
- Personal hygiene should be maintained.
- Any medicine for any pain should be taken as per the doctor's advice.
- Meaning of Conception and Fertilization:-
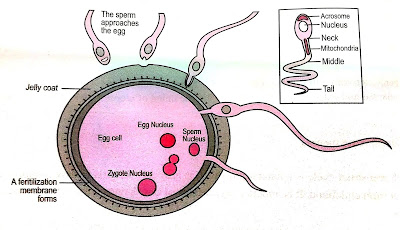
Fertilization is the process by which sperm and ova combine to create a single cell called a zygote. Fertilization occurs within 24 hrs after the ovum moves to the tube. The sperm are contained in a fluid called semen, which deposited at the neck of the womb during intercourse. The sperm is drawn up into the fallopian tube by hormonal attraction and muscular contraction. The sperm secrete an enzyme that disappears wall from around the ovum, once sperm reaches to ovum it penetrates the cytoplasm. This leads to change in the membrane of the ovum in such a way that no other sperm can now enter it.
Fertilized ovum slowly travels to the uterus and moves for 5-6 days in the uterus to find a place it gets implanted in the uterus walls of the uterus. This process is known as Implantation. The yolk sac is formed around the ovum cells until the implantation is completed as it provides nourishment to the ovum. Once the implantation process is over, yolk Sac disappears.
- Importance of Fertilization:-
Fertilization is most likely if intercourse occurs on the day of ovulation. If fertilization does not occur, the ovum and sperm cell in women body dies.
At the time of conception/Fertilization or few important things like the following are determined.
 2] Sex determination- Sex of the child is also confirmed at the time of conception. Among the 23 pairs of chromosomes, 22 pairs are called autosomes and one pair which is especially concerned with the determination of sex is called sex chromosomes. The sex chromosomes are either 'X chromosomes' or 'Y chromosomes'. The sex chromosomes of every ovum is an X chromosome, but the sperm may contain either an X or Y chromosomes. When an ovum [X] is fertilized by a sperm containing X chromosomes, the zygote formed has a pair of XX chromosomes. This composition is female, an organism is formed. When an ovum [X] is fertilized by sperm containing Y chromosomes, the zygote has XY pair and the male organism is formed.
2] Sex determination- Sex of the child is also confirmed at the time of conception. Among the 23 pairs of chromosomes, 22 pairs are called autosomes and one pair which is especially concerned with the determination of sex is called sex chromosomes. The sex chromosomes are either 'X chromosomes' or 'Y chromosomes'. The sex chromosomes of every ovum is an X chromosome, but the sperm may contain either an X or Y chromosomes. When an ovum [X] is fertilized by a sperm containing X chromosomes, the zygote formed has a pair of XX chromosomes. This composition is female, an organism is formed. When an ovum [X] is fertilized by sperm containing Y chromosomes, the zygote has XY pair and the male organism is formed.
At the time of conception/Fertilization or few important things like the following are determined.
- Heredity endowment
- Sex of the child
- Number of offsprings or children
1] Heredity endowment- This is an important factor influences development right from the prenatal stage. It is the genetic endowment inherited from biological parents at the time of conception. When ovum and sperm unite, they endow the baby to be with a genetic makeup that influences a wide range of characteristics such as the color of skin, hair, height, health, intellect, etc.
 2] Sex determination- Sex of the child is also confirmed at the time of conception. Among the 23 pairs of chromosomes, 22 pairs are called autosomes and one pair which is especially concerned with the determination of sex is called sex chromosomes. The sex chromosomes are either 'X chromosomes' or 'Y chromosomes'. The sex chromosomes of every ovum is an X chromosome, but the sperm may contain either an X or Y chromosomes. When an ovum [X] is fertilized by a sperm containing X chromosomes, the zygote formed has a pair of XX chromosomes. This composition is female, an organism is formed. When an ovum [X] is fertilized by sperm containing Y chromosomes, the zygote has XY pair and the male organism is formed.
2] Sex determination- Sex of the child is also confirmed at the time of conception. Among the 23 pairs of chromosomes, 22 pairs are called autosomes and one pair which is especially concerned with the determination of sex is called sex chromosomes. The sex chromosomes are either 'X chromosomes' or 'Y chromosomes'. The sex chromosomes of every ovum is an X chromosome, but the sperm may contain either an X or Y chromosomes. When an ovum [X] is fertilized by a sperm containing X chromosomes, the zygote formed has a pair of XX chromosomes. This composition is female, an organism is formed. When an ovum [X] is fertilized by sperm containing Y chromosomes, the zygote has XY pair and the male organism is formed.
It is clear that the sex of a child is decided by the chromosomes of the father. It is a natural process. Parents are not responsible for sex determination but the chromosome of the father determines the sex.
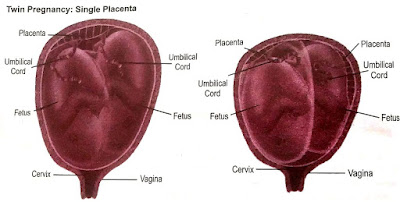
3] Number of Offspring- The important condition determined at the time of conception is whether the birth will be single or multiple. A term multiple refers to the birth of two or more babies in the same pregnancy. They can be twins, triplets, etc. Singletons are children who are born alone.
There are two types of twins; identical and non-identical [fraternal].
1-- Identical / Uni-ovular twins- Identical twins come from a single ovum fertilized by a single sperm,. They are formed from one fertilized ovum, they are of same-sex i.e, both boys, or girls
2-- Fraternal/ Non-identical twins- Two different ova fertilized by different sperm simultaneously. Such are fraternal twins. They can be of same-sex or different. Their genetic makeup is different.
Identical twins Fraternal Twins
There are two types of twins; identical and non-identical [fraternal].
1-- Identical / Uni-ovular twins- Identical twins come from a single ovum fertilized by a single sperm,. They are formed from one fertilized ovum, they are of same-sex i.e, both boys, or girls
2-- Fraternal/ Non-identical twins- Two different ova fertilized by different sperm simultaneously. Such are fraternal twins. They can be of same-sex or different. Their genetic makeup is different.
Identical twins Fraternal Twins
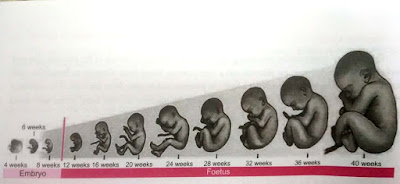
- Stages of Prenatal Development-
The prenatal period is a period of conception to birth. The length of this period is 280 days,38 weeks and 9 months.
This period is divided into 3 stages:-
This period is divided into 3 stages:-
- Period of Ovum [conception-2 weeks]
- Period of the embryo [ 3- 8 weeks]
- Period of the fetus [ 9 weeks till birth or 38 weeks]
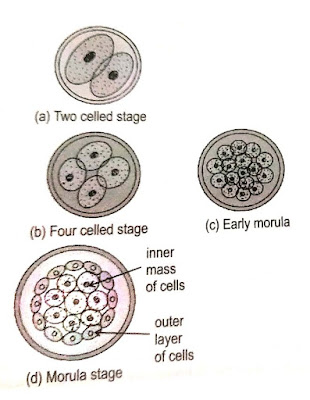
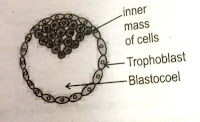
- Period of Ovum/ zygote [ conception- 2 weeks] This is a period about 2 weeks, from conception to implantation [fixation of the ovum in uterine walls]. Until the tiny mass of cells drifts down and out of the fallopian tube and attaches itself to the wall of the uterus. The fertilized egg is known as a zygote. The zygote's first duplication is a long process, it is not complete until about 30 hrs after conception. Then gradually, new cells are added faster rate. it starts dividing into 4,8,16 and then sub-divided into many cells. Finally, a cluster of many cells is formed which is known as "Morula". by the fourth day, 60-70 cells exist that form a hollow, fluid-filled ball, called a blastocyst. The next division of cells is within this cluster where a small cavity is formed and gets into a stage of the "Blastula stage". The cells on the inside called the embryonic disk will become a new organism, the outer ring provide protective coverage. This travels to the uterus and gets implanted. Sometimes, it gets implanted into the fallopian tube which is called tubal/ ectopic pregnancy. The tube gets ruptured due to the growth of the embryo which leads the bleeding. In such cases, the embryo is removed by surgery.
Implantation, sometimes between the 7 and 9 days, it occurs: the zygote burrows into the uterine wall and established a connection with the mother's blood vessels. This blastocyst burrows deep into the uterine lining. surrounded by the women's nourishing blood. When implantation takes place there are some hormonal changes that prevent menstruation which lets women know that she has conceived. At first, the protective outer layer multiplies the fastest. A membrane called amnion is formed that encloses the developing organism in amniotic fluid. It helps to keep the temperature of the prenatal world constant and provides a cushion against any jolts caused by the mother's movement. A yolk sac also appears. It produces blood cells until the developing liver, spleen, and bone marrow are mature enough to take over this function. The events of these 2 weeks are delicate and uncertain. As many as 30% of zygotes do not make it through this phase. In some, the sperm and ovum do not join properly. By preventing implantation in these cases, nature eliminates most prenatal abnormalities in the very early stages of development.
The placenta and Umbilical cord- By the end of the second week, another protective membrane, called Chorion, surrounds the amnion. From the chorion, tiny finger-like villi, or blood vessels begins to emerge. As these villi burrow into the uterine walls, a special organ called placenta starts to develop. By bringing the mother's and embryo's blood close together, the placenta will permit food and oxygen to reach the developing organism and waste products to be carried away. A membrane forms that allow these substances to be exchanged but prevents the mother's and embryo's blood from mixing directly. The placenta is connected to the developing baby by the umbilical cord. which develops in further stages. The umbilical cord contains one large artery that delivers blood loaded with nutrients and two veins that remove waste products. The force of blood flowing through the cord keeps it firm, much like space-walking astronauts, floats freely in its fluid-filled chamber. By the end of the Period of Zygote, the developing organism has found food and shelter in the uterus. These dramatic beginnings take place before all but the most sensitive mother knows that she is pregnant.
- Period of Embryo- [3-8 weeks] The period of embryo lasts from implantation through the eight weeks of pregnancy. In this period, the internal organs and body structures of the embryo develop. During these brief 6 weeks, the most rapid prenatal changes take place as the groundwork for all body structures, and internal organs are laid down. Because all parts of the body are forming, the embryo is especially vulnerable to interference in healthy development. But the fact is that embryonic growth takes place quickly, over a short time span, limits opportunities for serious harm to occur. Growth Of Embryo-
Last half of the first month- In the first week of this period, the embryonic disk differentiates into 3 layers of cells, which are:-
- Ectoderm [outer layer]- It forms the skins, nails, hair, teeth, sensory organs, brain, spinal cord, etc. All surface parts of the body developed from this layer.
- Mesoderm [middle layer]- It forms the skeleton, circulatory system, reproductive system, i.e. the parts that surround internal areas of the body are formed from these layers.
- Endoderm [inner layer]- It forms the lungs, digestive system, urinary tract. i.e. Formation of internal body parts. The period of an embryo is marked by the development of vital organs and other body structures called 'organogenesis'. These three layers give rise to all parts of the body. At first, the nervous system develops faster. At 3 and a half weeks, the top swells to form a brain, the production of neurons begins inside the neural tube. While the nervous system is developing, the heart begins to pump blood around the embryo's circulatory system, and muscles, backbone, ribs, the digestive tract start appear. At the end of 1 month, the curled embryo consists of millions of an organized group of cells with specific functions, although it is only 1/4 of an inch long. The Second Month- In the second moth grow continuos rapidly. The eyes, ears, nose, jaw, neck form. Tiny buds become arms, legs, fingers, and toes. Internal organs are more distinct. The intestine grows, the heart develops separate chambers, and the liver and spleen take over the production of blood cells so that the yolk sac is no longer needed. This changes the body proportion of the embryo. Now inch long and one-seventh of an ounce in weight, the embryo can already sense its world. In response to touch particularly in the areas of the mouth and on the soles of the feet. And it can move, although its tinny flutters are still too light to be felt by the mother.
3] Period of Foetus [9 weeks till birth]-
Lasting until the end of pregnancy, the period of the fetus is the "growth and finishing" phase. During this longest prenatal period, the developing organism begins to increase rapidly in size.
*The third month- In the 3rd month, the organs, muscles, and nervous system start to become organized and connected. The brain signals and in response, the fetus kicks, bends its arms, form a fist, curls its toes, open its mouth, and even such the thumb. The tiny lungs begin to expand and contract in an early rehearsal of breathing movement. By 12 weeks, the external genitals are well-formed, and the sex of the fetus is evident. Other finishing touches appear, such as fingernails, toenails, tooth buds, and eyelids open and close. The heartbeat is now stronger and the doctor can hear through a stethoscope.
Prenatal development is divided into trimester or 3 equal periods of time. at the end of 3 months, the first trimester is completed. The two more must pass before is fully prepared to survive outside the womb.
* The second Trimester- Between 17 and 20 weeks age, the new being has grown large enough that its movements can be felt by the mother. In the uterus, the fetus is fully covered with white cheeselike substances called Vernix. It protects the skin from chapping during the long months spent bathing in the amniotic fluid. A white, downy hair covering called lanugo also appears over the entire body, helping the vernix strick to skin.
At the end of the second trimester, many organs are quite well developed. In brain development, all neurons are now in place. No kore will be produced in the individual's lifetime. However, glial cells, which supports and feed neurons, continue to increase at a rapid rate throughout the remaining months of pregnancy, as well as after birth. The 20 weeks old fetus can be stimulated as well as irritated by sounds. And if a doctor has reason to look inside the uterus with fetoscopy, fetuses try to shield their eyes from the light with their hands, indicating that sense of sight has begun to emerge. Still, a fetus born at this time cannot survive. Its slings are quite immature, and the brain is yet to developed to the point at which it can control breathing movements and body temperature.
*The Third Trimester- The final trimester of the pregnancy differs from the previous 6 months in that if born early, the fetus now has changed for survival outside the womb. It is because called the age of Viability. It occurs sometimes between 22 and 26 weeks. If born between 7 and 8 months, breathing would still be a problem, and oxygen assistance would be necessary. Although the respiratory center of a brain is now mature, tiny air sacs in the lungs are not yet ready to inflate and exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. At this time, the fetus responds more clearly to sounds in the external world. The fetus reaches with a forceful startle. By 28 weeks, fetuses blink their eyes in reaction to nearby sounds. In the last weeks of pregnancy, they learn to prefer the tone and rhythm of their mother's voice.
During the final 3 trimesters, the fetuses gain more than 5 pounds and grow 7 inches. As it fills the uterus, it gradually becomes less active. In 8 months, a layer of fat added under its skin to assist with temperature regulation. The fetus also receives antibodies from the mother's blood that protect it from illnesses that could be dangerous to the newborn, whose immune system will not work well until several months after birth. In the last weeks, most fetuses assume an upside-down position, because of the shape of the uterus and because the head is heavier than feet. The growth of the fetus starts to slow, and birth is about to take place. The length is about 50 cm and the weight is 2600 to 3500gm. Skin is smooth and pink, digestive, respiratory, circulatory system are fully developed. Baby is fully developed and capable of living in the outside world.
Importance of Fetal period- Major parts of the body are completed un a rudimentary form. Since the nervous system is maturing, mental growth may be affected, if there are any adverse conditions. Any deficiency in nutrition can cause unsound teeth and jaw face defects. The danger of miscarriages depends on prenatal conditions. Moreover the attitude of the mother, her anxiety, etc. can affect the birth and delivery process.
Overview- The vast changes that take place during pregnancy are usually divided into three trimesters. In the period of the zygote, the tiny- one called fertilized ovum begins to duplicate and implants itself in the uterine lining. Structures that will feed and protect the developing organism begins to form. During the period of the embryo, the foundations for all body tissues and organs are rapidly laid down. The longest prenatal phase, the period of fetal development, is devoted to growth in size and completion of body systems.
During the final 3 trimesters, the fetuses gain more than 5 pounds and grow 7 inches. As it fills the uterus, it gradually becomes less active. In 8 months, a layer of fat added under its skin to assist with temperature regulation. The fetus also receives antibodies from the mother's blood that protect it from illnesses that could be dangerous to the newborn, whose immune system will not work well until several months after birth. In the last weeks, most fetuses assume an upside-down position, because of the shape of the uterus and because the head is heavier than feet. The growth of the fetus starts to slow, and birth is about to take place. The length is about 50 cm and the weight is 2600 to 3500gm. Skin is smooth and pink, digestive, respiratory, circulatory system are fully developed. Baby is fully developed and capable of living in the outside world.
Importance of Fetal period- Major parts of the body are completed un a rudimentary form. Since the nervous system is maturing, mental growth may be affected, if there are any adverse conditions. Any deficiency in nutrition can cause unsound teeth and jaw face defects. The danger of miscarriages depends on prenatal conditions. Moreover the attitude of the mother, her anxiety, etc. can affect the birth and delivery process.









Nice
ReplyDelete