- Why Have Children?
The reason for having children is dependant on the couple only. In India, children are very important for married couples. In India, marriage and family are an important social institution. as the primary function of marriage in India is to procreate and upbringing of children. The main aim of marriage is to establish a family. Earlier the children are very important for any couple and childless couple especially women are treated as taboo for society and treated as evil. But as the status of women changed a lot of changes one can be observed in the family patterns. Nowadays, a couple can decide their parenthood, or whether they want to become a parent or not, they can also go for a sterilization process. The earlier couple decided to have more children as it becomes their working hands and boosts the family's economic conditions. But nowadays, the number of children is decreased and a couple decided to have single children's families or two children or childlessness. Effective birth control techniques help to avoid accidental parenthood and help in family planning. The reason for the desire of children is different for every couple. For some, it is family pressure, religious needs, for a growing family, the couple believes that children can increase couple love and some believe that it is not true.etc. for certain couples having children means extra burden and responsibilities, loss of freedom, financial strain are the biggest disadvantages of parenthood for many couples. So there are various pros and cons of parenthood. But nowadays, many couples are making personal choices about becoming parents.
Benefits and cons of Parenthood
Benefits·
·
Giving and receiving warmth and affection
·
Experiencing the stimulation and fun that children add
to life
·
Learning to become less selfish and to sacrifice.
·
Being accepted as a responsible and mature member if
the community
·
Experiencing new growth and learning opportunities
that add meaning to life
·
Gaining a sense of accomplishment and creativity from
helping children grew
·
Helping in old age
Cons
o
Loss of freedom, being tied down
o
Financial strain
o
Fear that children will turn out badly
o
Worries over children’s health, safety, and
wellbeing.
o
Loss of Privacy
o
Risks of bringing up children in a world plagued
by crime, war, and pollution
o
Reduced time to spend with husband or wife
o
Interference with career, mainly of the mother.
o
Lots of adjustment difficulties related to
money, the Sex life of parents, household work, social adjustments, etc.
- How large the family is?
Earlier having children in India is directly connected with the economy. Too many working hands means lots of financial help. But in modern times where the family pattern is nuclear so couple prefers, single or 2 children. Those who live in a joint family may prefer more than 2 kids. But many researches have proved that it is a benefit for children to grow in small families. Parents who have fewer children are more patient and useless punishments. They also have more time to devote to each child's activities, school work, and other special needs. Together these findings may account for the fact that children who grow up in smaller families have somewhat higher intelligence test scores, do better in schools, and achieve independence earlier.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the one-child family
Advantages
Mentioned by Parents
|
Mentioned by Children
|
·
Having time to pursue one’s own interests and career.
|
·
Avoiding sibling rivalry
|
·
Less financial pressure
|
·
Having more privacy
|
·
Not having to worry about “playing favorites” among children.
|
·
Having a closer parent-child relationship.
|
Dis-advantages
Mentioned by Parents
|
Mentioned by Children
|
·
It is difficult to distinguish between healthy attention and overindulgence/over protection.
|
·
Not getting to experience the closeness of a sibling relationship.
|
·
Having only one chance to practice healthy parenting skills.
|
·
Feeling too much pressure from parents to succeed.
|
·
Being left childless in case of a child’s career, after child’s marriage or child’s death.
|
·
Difficult to share everything with parents because of the generation gap.
|
·
Career-oriented parents make the child feel lonely and indulge in bad
habits.
|
- Best time for having Children?
If we talk about Indian couples, as we already read that the main aim of marriage is family planning. An earlier, when child marriage was high at the peak at that time, parents think that as soon as a girl achieves puberty it is a sign as she is ready to give birth to the child, that's why child marriage practice a lot. But due to Industrialization, Urbanization, lot's of technological advancements changed the mindset of the people. Many doctors proved that 23 to 25 was the ideal age of becoming a mother. Many women also become a mother in the late '30s.
Nowadays, many couples are putting off childbearing until their careers are well established and they know they can support a child. Older parents may be somewhat less energetic than they wee at ana earlier age, but they are financially better off and more emotionally mature. Yes, fertility does decline with age. Older women who want to have children may find it more difficult to conceive, and also a greater number of miscarriages occur with advancing age. the couples who decide to put off child-birth until well into their 30 or early 40 do risk the possibility that they may not have children. Many couples nowadays, as women are empowered and are career-oriented so they mainly opt for adoption or Surrogacy.
Prenatal Period:-
prenatal period refers to the period from conception to the birth of a child. The fertilization of the egg cell, ovum by the sperm is a starting point of the new life. A sperm penetrates into the egg cell which is known as fertilization or conception. Prenatal development refers to the process in which a baby develops from a single cell after conception into an embryo and later a fetus.
The average length of time for prenatal development to complete is 36-38 weeks from the date of conception/Fertilization. During this time, a single cell zygote develops in a series of stages into a full-term baby. In order to understand the above process, we need to understand the male and female reproductive system and its functioning.
- Fertilization is the process by which sperm and ova combine to create a single cell called a zygote. Fertilization occurs within 24 hrs after the ovum moves to the tube. The sperm are contained in a fluid called semen, which deposited at the neck of the womb during intercourse. The sperm is drawn up into the fallopian tube by hormonal attraction and muscular contraction. The sperm secrete an enzyme that disappears wall from around the ovum, once sperm reaches to ovum it penetrates the cytoplasm. This leads to change in the membrane of the ovum in such a way that no other sperm can now enter it. Fertilized ovum slowly travels to the uterus and moves for 5-6 days in the uterus to find a place it gets implanted in the uterus walls of the uterus. This process is known as Implantation. The yolk sac is formed around the ovum cells until the implantation is completed as it provides nourishment to the ovum. Once the implantation process is over, yolk Sac disappears.
In order to understand the above process, we need to understand the male and female reproductive system and its functioning.
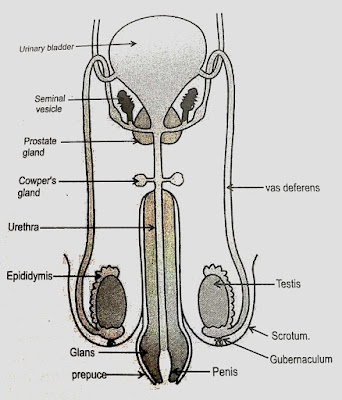
- Male Reproductive system
The male reproductive system consists of penis, scrotum, testes, epididymis, vas deferens, urethra, prostate gland, and seminal vesicles. - Penis- Penis is a Latin word meaning tail. It is the main sexual organs made of glans, shaft, and root. It is composed of spongy like tissues. The urethra passes through the penis i.e. it is surrounded by erectile tissue. When the tissue becomes engorged with the blood the penis becomes erect and rigid. The root is attached to the wall of the abdomen; the body is the shaft, and the glans are the cone-shaped end of the penis. The glans, which is also called as head of the penis, is covered with a loose layer of skin called the foreskin. The opening of the urethra, the tube that transports semen and urine, is the time of the glans. The penis also contains a number of sensitive nerve endings.
- Scrotum- The scrotum is a loose pouch-like sac of the skin, on either side of the penis. It contains the testicles [testes], as well as many nerves and blood vessels. The scrotum act as a climate control system for the testes. For normal sperm development, the testes must be at a temperature slightly cooler than the body temperature.
- Testes- They lie in the scrotum, the two major functions of testes are:-to produce sperm and to produce male hormone- testosterone. Inside the testes are a number of tubes called seminiferous tubules. These are responsible for producing sperm cells.
Male Reproductive System
- Epididymis- It is a long, coiled tube that rests on the backside of each testis. It helps in the transport and storage of the sperm cells that are produced in the testes. The function is to bring the sperm to maturity since the sperms that emerge from the testes are immature and incapable of fertilization. During sexual intercourse, contractions force the sperm into the vas deference. The average length of the epididymis in 20 feet.
- Vas deferens- A continuation of Epididymis. It travels from epididymis into the pelvic cavity, just behind the bladder. It joins the prostrate, receiving secretions from the seminal vesicle, the prostate, and bulbourethral glands. The vas deference opens into the urethra. It transports mature sperm to the urethra in preparation for ejaculations.
- Urethra- The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside of the body. In males, it has the additional functioning of ejaculating semen, when the man reaches orgasm. When the penis is erect during sex, the flow of urine is blocked from the urethra, allowing only semen to be ejaculated at orgasm.
- Prostate gland- It is a walnut-sized structure that is located below the urinary bladder in from of the rectum. The prostate gland contributes additional fluid to ejaculate. It also helps to nourish the sperm. The urethra, which carries the sperm to be expelled during orgasm, runs through the center of the prostate gland.
- Seminal vesicles- It is situated on the side or near the base of the bladder. Their ducts pass through the prostate and into the urethra. The seminal vesicles store sperms and produce a sugar-rich fluid [fructose] that provides sperms with a source of energy and helps with the sperm's motility. The fluid of seminal vesicles makes up most of the volume of a man's ejaculatory fluid, or ejaculations.
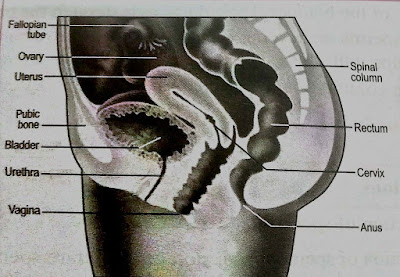
- Female Reproductive System
A female reproductive system is created to carry out certain functions. It produces the female egg cells necessary for reproduction, called ova. The system is designed to transport the ova to the site of fertilization. Conception, the fertilization of an egg by a sperm, normally occurs in the fallopian tube. After conception, the baby develops in the uterus which is a safe and favorable environment, before it makes the way into the outside world. If fertilization does not take place than menstruation occurs, [ the monthly shedding of the uterine lining]. The female reproductive system also produces female sex hormones that maintain the reproductive cycle. Female reproductive includes external and internal structures. To enable the sperms to enter the body and to protect the internal genital organs from the infectious organisms. The main external, organs of the female reproductive system include:
- Labia majora- The labia majora encloses and protects other external reproductive organs. It means large lips, After puberty, the labia majora are covered with hair.
- Labia minora- It means small lips, They lie just inside the labia majora, and surrounded the openings to the vagina and urethra.
- Clitoris- Labia majora and Labia minora meet at what is called the clitoris, which is very sensitive to stimulation and becomes erect.
The female internal organs consist of pf Ovaries/gonads, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Vagina.
Female Reproductive System
- Uterus- It is a small hollow muscular organ. Its size and shape are of inverted pear. Placed at the top of the Vagina. It is placed between the bladder in front and rectum behind. Its width is 5cm, the length is 7.5cm and the thickness is 2- 2.5cm. The weight of the uterus is 50-60 grams.
- Vagina- It is a hollow tube. its length is around 7-10 cm. The upper part of Vagina is divided into anterior, posterior, right and left lateral. At the lower end of fold known as HYMEN, It receives the erect penis during intercourse. It allows the passage of menstrual flow. It serves as a birth canal. The function od Vagina is to absorb the sperm of men during intercourse, to expel menstrual shedding and to give birth to a baby.
- Fallopian and uterine tubes- To the right and left of the uterus are two tubes; each is 10-12 cm long. The tube is narrow where it enters the uterus and wide at its outer end close to the ovary. The muscles in the tube are arranged such that the contents are squeezed into the uterus. The outer end has a number of fingers like projections which stretch towards the ovary and pick up the egg cell. Fertilization occurs in the tube after which the fertilized egg is passed into the uterus.
- Ovaries- Ovaries lie on each side of the pelvis, near to the outer end of the uterine tubes. Ovaries are connected to the uterus by an ovarian ligament. They are hollow almond-shaped. The length is 3 cm, width 2 cm, and the thickness is 1 cm. Ovaries serve two functions, #They produce egg cell ova and # Produce female hormone- estrogen and progesterone.
Each ovary contains about 200 thousand ova in early life but they decrease with age and disappear after menopause. Apprx, around 400 actually develop and released at monthly intervals into the uterine tubes from the time of menarche till menopause.










No comments:
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link into comment box.